Full Stack Development: A Short Guide to Get You Started

The Full-Stack Developer role is a rare, yet achievable role. It combines both front-end and back-end development to bring you a powerhouse developer who is proficient at doing both. While not an expert, there are a lot of redeeming qualities that a Full Stack Developer brings to the table.
Let’s see what Full Stack Development is all about and how you can become a Full Stack Developer.
What is Full Stack Development?
Full Stack Development (FSD) is a development process used for developing both the frontend and the backend of a software. A Full Stack Developer knows how to design and develop the front end while also knowing how to design, develop, and debug databases and the backend of the software.
You might already be wondering if such a developer is a jack of all trades. Well, you would be right since an FSD is usually a senior position that makes you go back and forth between the two ends of the development spectrum.
Full Stack Development: The Technologies
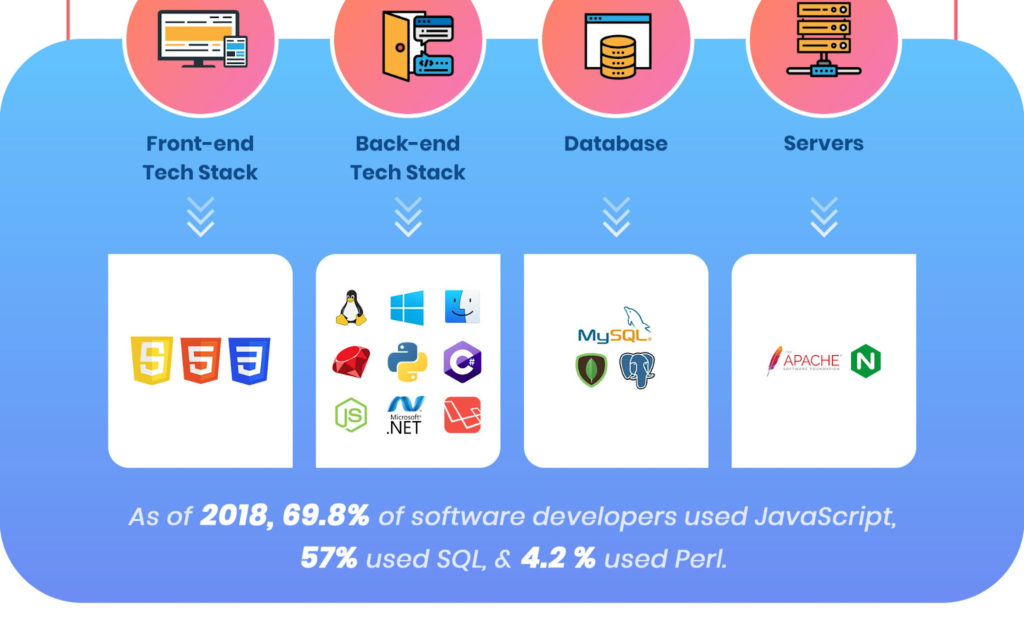
We mentioned that FSD’s are the jacks of all trades. Let’s show you a glimpse of what that means. The list of technologies FSD’s use is enough to tell you how valuable an FSD is to a software business.
Front-End:
If you’re new to all of this: the front end is the part of the software that the user can view and interact with.
Take an app for example. You open up the app and it leads to a login screen. You make an account on the app by interacting with the various buttons. That’s all the front-end in its purest form.
Your account registration, password, username, and everything else you entered are stored in the backend, but that’s an example for the next section of this post.
Front-End Development Languages
Powering up that front-end is a group of programming languages. Well, they’re markup and scripting languages but for the sake of simplicity and generalization, let’s just call them programming languages.
If you’re looking for or wanting to become an FSD, then these languages are essential. You can’t become one without knowing these.
HTML: Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the root of the internet. It’s the proverbial skeleton of every website, software, or mobile app. The language uses tags that the browser or an API uses to interpret on a user’s screen.
CSS: Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) comes immediately after HTML in that it adds color and style to the website. If HTML is the skeleton, then this is the muscle and skin. It adds aesthetic design to a website by applying styles. Every design element you see on a website or application is made with CSS or a rendition of it.
JavaScript (JS): A scripting language used to add functionality and interactivity to a website. The language is an expansive one, allowing you to make games, websites, applications, and so much more.
PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor, aka PHP, is a programming language used to add pretty much the same functionality as JavaScript. The only difference between PHP and JavaScript is the usage. PHP was famous in the years gone by and is still relevant because it’s used in the legacy code of most modern businesses. JavaScript is relatively new yet its range of frameworks and libraries make the development experience much more controlled and error-free.
Front End Frameworks and Libraries
What are front-end frameworks, you might ask? Well, think of them as a structure that you use to develop your applications and websites more quickly and efficiently. Almost every major programming language comes with a framework because it makes the work easier. In JavaScript, you have several frameworks that make the front-end development experience much more optimized. Here’s a list of popular front-end frameworks:
- React JS and Angular JS.
- Sass and Less for CSS.
- Bootstrap for HTML and CSS.
- jQuery for JavaScript.
- Backbone JS.
- Materialize UI.
And many more.
Also Read:
- Java vs .NET – Which is Better for Software Developers? A Beginners Guide
- SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS: What You Need to Know with Examples
- PHP vs JavaScript For Web Development
Front-End Development’s Miscellaneous Requirements
Besides the languages, there are several other considerations when it comes to front-end development.
- Understanding design theory and the design elements required for an optimal user experience.
- Knowledge of Git, GitHub, and other code repositories.
- Knowing how to use sass, less, and other pre-processors.
- Basics to advanced uses of code editing programs like visual studio, sublime text, and atom.
Back-End:
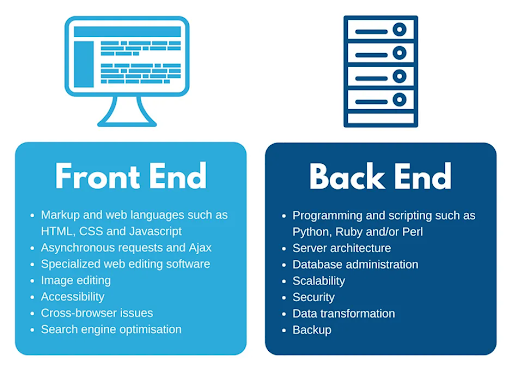
In developer speak, the backend is quite literally the backend of a website. It’s the server-side of web development that includes managing the databases and backend functionality. Its primary goal is to add interactivity and functionality to the front-end. It’s what makes a website get its life.
Similar to the front-end, the backend also has some cool programming languages that you can use. Let’s take a look at some of them, shall we?
PHP: Before you say anything, just know that PHP and JavaScript are considered both front and backend languages. Okay, so we’ve already discussed PHP as a language. Its primary function in the backend is to execute the code which is why it’s called a server-side scripting language.
C++: Not to be confused with the dreaded C language, C++ is a much easier and general-purpose programming language that, without going into too many details, is pretty handy when it comes to creating a robust backend.
Java: you’ve played the games coded in this language. Yes, java is still a popular general-purpose language with it being scalable and open source.
Python: The easiest yet robust language is the list, Python is a general-purpose programming language that’s used in many modern software systems today. Because of its ease of use, it’s a choice for many beginners looking to enter into the front-end development scene.
JavaScript: Used for the server end and adding front-end functionality, it’s a language that’s now being used in websites and software programs more than PHP in comparison.
Backend Frameworks
Besides the major languages, there are plenty of frameworks present for them that make the workflows easier. Let’s give you a list:
- Node JS (JavaScript)
- CodeIgniter (PHP)
- Laravel (PHP)
- Django (Python)
And more.
Sidenote: If you’re a newbie, what should you start with? Well, in most scenarios learning JavaScript can be a useful first programming language.
A lot of people will recommend Python and it’s not bad. Our justification for this is that because JS is used in the back and front-end, it becomes a good enough language to use.

Databases:
Databases are an important part of the software development process. It’s the place where all the data is stored, retrieved, and processed in, ready to be fetched at any particular time.
For a Full Stack Developer, having an understanding of databases is a must.
You need to know the basics of how databases work and more importantly, have command over specific database languages. Let’s look at a list of popular databases.
- Oracle
- MongoDB
- SQL
There are other database platforms out there, but these are the more popular ones. It pays to learn them first and foremost.
Now, on to the more important questions.
Why Do Companies Need a Full Stack Developer?
There are plenty of reasons why you need a jack of all trades on your team. For a software development company, you need a Full Stack professional for the following:
- Because of their knowledge of both ends of the spectrum, they can offer their expertise in both development cycles to keep the processes smooth.
- By taking estimates of both development cycles, FSDs can implement accurate periods for a project’s completion.
- They’re useful in reducing operational costs, and if you’re a startup, then it saves on infrastructure costs.
Skills required for Full Stack Development
We’re reiterating a bit, but you need the following to have a complete grasp of Full Stack Development.
- Front-End Technologies: JavaScript, CSS, HTML, and its associated frameworks.
- Server-side programming languages: Python, ruby, .net, java, and others.
- Databases: MongoDB, SQL, and others.
- Web Design: A basic understanding of design theory, UI/UX, and colors can prove very beneficial for cementing your role as an FSD.
- Servers: Knowing how servers work to store, process, and fetch data from the server to the front-end.
- Version Control: Git, GitHub and other code repositories and how they work to manage the codebases and updates.
- APIs: understanding web services and APIs and how they integrate with the software.
Besides that, you need to know basic programming concepts like algorithms and understanding how to write unit tests for quality assurance.
If you’re looking to go full-stack, then we’d recommend checking out this nice infographic that details what you need to know to become a Full Stack Developer.
Software Stacks: What They Are and Which One Should You Learn
If you’ve been in the development sphere for some time now, you’d know of some terms like the MEAN stack and the LAMP stack.
Before we go on to explain what they stand for, it’s important to know what a technology stack is.
It’s a group of programming languages, frameworks, and libraries working together for a particular result. A phone has an OS, a browser, and some basic applications when you first start it up.
Based on your career goals, your Full Stack technology stack can contain a combination of technologies that you would add to the stack.
Now, they aren’t unrelated to one another and you would find a lot of similarities in the architecture of the applications.
LAMP stack
Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP – that’s what the letters in the LAMP stand for. Primarily used for web services development, it’s an ideal model for web service stacks. The LAMP stack and others are used by solutions like Facebook.
MERN stack
If the LAMP stack is PHP-oriented, then the MERN stack is its exact opposite. MERN stands for MongoDB, ExpressJS, ReactJS, and NodeJS. For the development of web applications, there is no better solution than the MERN stack.
MEAN stack
The MEAN stack is seeing a resurgence in its usage. MEAN stands for MongoDB, ExpressJS, AngularJS, And NodeJS.
All of these have their usage in developing a web application but they are, at their core, similar in terms of the core architecture.
Full Stack Developer Responsibilities and Requirements
This one’s for the HR managers and the employers, but for a Full Stack Developer, this resource can prove just as useful.
Responsibilities
- Working alongside product development teams to solve development issues and coming up with ideas.
- Creating client and Server End architecture.
- Building the Front-End and the User Experience.
- Managing the back-end of the applications.
- Writing APIs efficiently.
- Unit testing the software for efficiency.
- Writing technical documentation.
- Checking data and making changes to the product as necessary.
Requirements
- Proven Full Stack Development experience.
- Understanding of common technology stacks.
- Understanding of front-end languages like JavaScript, HTML, CSS, XML, and jQuery.
- Knowledge of multiple backend languages like PHP, Python, C#, and others.
- Knowledge of databases like SQL, MongoDB, and web servers like Apache.
- Ability to work as part of a team.
- Excellent communication skills.
- Attention to detail.
- Degree or certification in Computer Science or a related field.
Full-Stack Developer Salary by Country
We’ve developed this infographic to help you understand the varying salaries of a Full Stack Developer based on country.
- SWITZERLAND: $106K/YEAR (CHF 95K/YEAR)
- DENMARK: $84K/YEAR (DKK 516K/YEAR)
- AUSTRALIA: $77K/YEAR (A$100K/YEAR)
- UNITED KINGDOM: $76K/YEAR (£54K/YEAR)
- THE NETHERLANDS: $76K/YEAR (€63K/YEAR)
- GERMANY: $70K/YEAR (€58K/YEAR)
- NORWAY: $65K/YEAR (540K/YEAR KR)
- AUSTRIA: $63K/YEAR (€52K/YEAR)
- SWEDEN: $63K/YEAR (SEK 528K)
- IRELAND: $62K/YEAR (€51K/YEAR)
- CANADA: $60K/YEAR (CA$73K/YEAR)
- FINLAND: $57K/YEAR (€47K/YEAR)
- FRANCE: $53K/YEAR (€44K/YEAR)
- SINGAPORE: $46K/YEAR (S$62K/YEAR)
- ITALY: $39K/YEAR (€32K/YEAR)
- RUSSIA: $38K/YEAR (2.76M/YEAR)
- SPAIN: $38K/YEAR (€31K/YEAR)
- CHINA: $37K/YEAR (CN¥235K/YEAR)
- PORTUGAL: $20K/YEAR (€16K/YEAR)
- ROMANIA: $18K/YEAR (RON 72K/YEAR)
- BULGARIA: $18K/YEAR (BGN 30K/YEAR)
- MEXICO: $14K/YEAR ($288K/YEAR MXN)
- INDIA: $8K/YEAR (₹600K/YEAR)
- INDONESIA: $5K/YEAR (RP 78M/YEAR)
- UKRAINE: $1K/YEAR (₴26K/YEAR)
Is It Worth It to Become a Full-Stack Developer in 2021?
Yes, it’s worth it. You see, the Full Stack profession doesn’t keep you bound in one place. Instead, it gives you a multi-faceted role that gives you two hats to work with.
Of course, you want to ensure that you have an understanding of the various concepts of both the development ends to ensure an optimal development experience.
If you’re so proficient in what you do, you will be an asset since you can do both the works while not staying in one place.
The ideal setting for a Full Stack Developer is when they switch back and forth. Word of warning: if you’re not getting that balance, then you should generally avoid such a job.
If you’re looking to hire Full Stack Developers for your next project, then you should contact Codup. Our professional web developers will take care of your project as their own.


